Cities are complex entities but stripped to the basics, they consist of people & communities that interact with objects such as roads, buildings, and spaces, across a broad range of settings and contexts. And when cities are called smart cities, it means that various sensors collect data to get insights and use them to manage these objects efficiently. If we think of them as assets, then sound asset management must have real benefits. Minimizing asset downtime and increasing asset life expectancy being two examples. These translate into higher performance, lower management costs, happier asset users, and better sustainability. How smart cities are using Artificial Intelligence, then?
In the cites, there are various types of issues:
- proactive maintenance,
- prioritization of work,
- infrastructure condition assessment,
- damaged roads, pylons, buildings, etc.,
- blind spots on assets & conditions,
- maintenance cost optimization.
To manage the maintenance of these critical assets, we need to obtain budgetary estimates for ongoing maintenance. It is crucial to establish a process that identifies damage as early as possible. Identifying surface damage and signs such as cracking, potholes, subsidence, or erosion are often the first indicators that urgent remedial action is required.
That’s why, the resources needed to assess road conditions are traditionally very high, demanding considerable amounts of labor (manual surveying usually) and complex project planning to avoid mismanagement of valuable and scarce resources & inappropriate or inefficient budget allocation. Among other types of assets that are common in the cities, there are buildings utility structures such as power transformers, pylons and microwave towers or phone poles, rails, gasometers, and pumping stations.
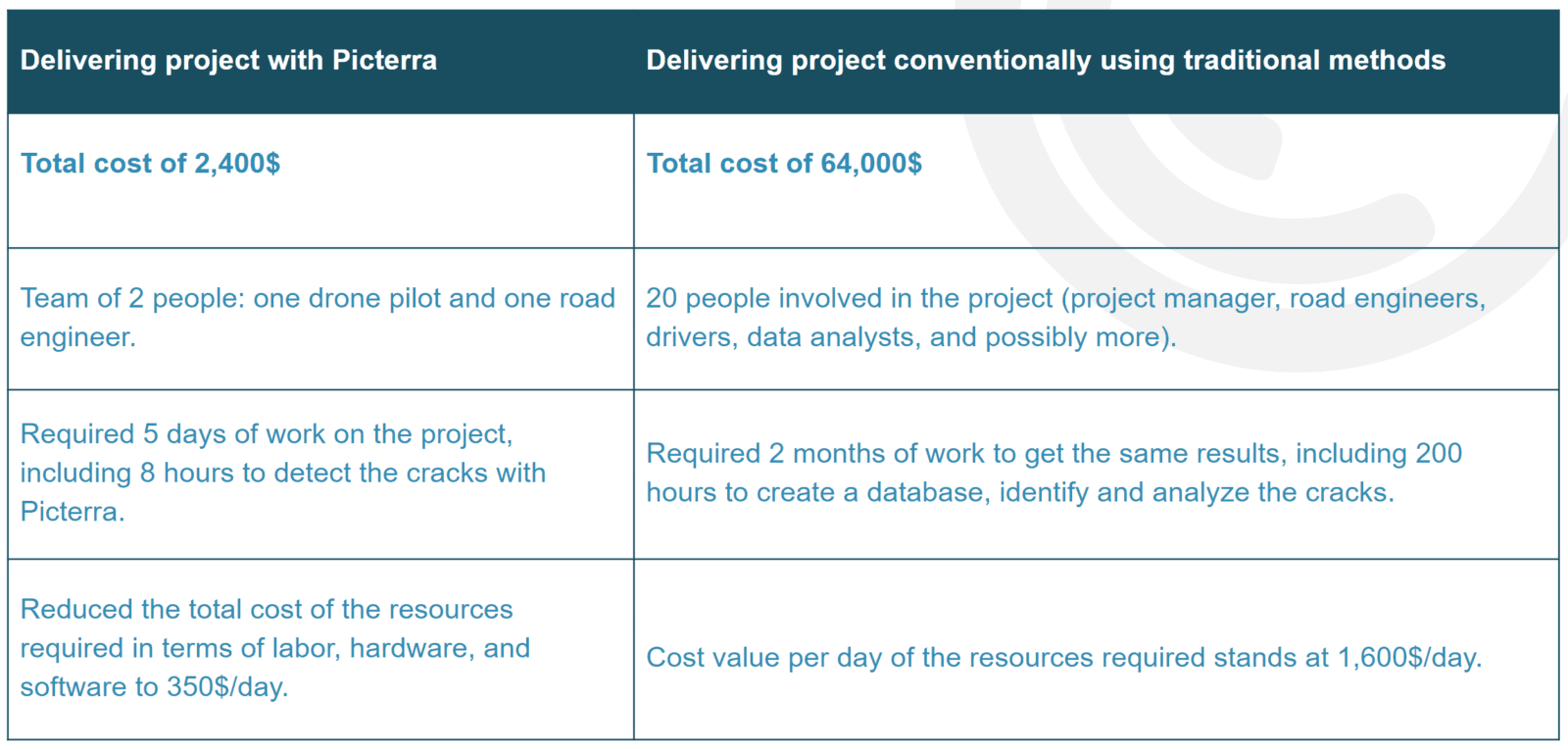
To give you a real-life example, Picterra was used to monitor and optimize road maintenance costs in the city of Kokomo, Indiana, USA. The purpose of this project has been to:
- Allow the city council to manage road maintenance costs preemptively.
- Optimally map public fund utilization priorities for renovation or construction.
- Provide a methodology for all future public infrastructure maintenance efforts.

The results have been highly promising.
Do you want to learn more about smart cities are using Artificial Intelligence?
On 2 April 2020, we hosted a webinar where our experts presented how smart cities are using Artificial Intelligence and demonstrated real-life examples. The recording is available below.
How smart cities are using Artificial Intelligence?
There are different steps where machine learning can play a role. At first, AI in the context of Eart Observation imagery allows extracting geospatial features to be used in maps and GIS software in an automated way. However, it is good to mention the other areas that come after this first stage of extraction, such as the analysis of spatial-temporal urban patterns (urban growth, infrastructure deployment, mobility and neighborhood relations, etc.). And finally, with geospatial patterns enriched with attribute metadata, for example, information on building usage, transportation timetables, etc. can be feed to AI&ML to analyze trends and heterogeneities present in a city.
There are different steps where machine learning can play a role. At first, AI in the context of Earth Observation imagery allows extracting geospatial features to be used in maps and GIS software in an automated way. However, it is good to mention the other areas that come after this first stage of extraction: for example, the analysis of spatial-temporal urban patterns (urban growth, infrastructure deployment, mobility and neighborhood relations, etc.). And finally, with geospatial patterns enriched with attribute metadata, for example, information on building usage, transportation timetables, etc. can be feed to AI&ML to analyze trends and heterogeneities present in a city.
Picterra facilitates it by providing an intuitive and easy to use platform that makes geospatial imagery analysis easy. Here are just a few examples of projects done using the Picterra platform. It’s not a comprehensive list – more different objects can be detected.
- buildings,
- building foundations,
- slam buildings,
- informal settlements,
- damaged buildings,
- fire damages,
- stone walls,
- roof windows,
- solar panels,
- roof objects,
- chimneys,
- air conditioners,
- water coolers,
- water tanks,
- swimming pools,
- waste, trash,
- roads,
- road cracks,
- various road features, such as crocodile cracks, cracks intersections, potholes,
- road markings, such as crosswalks, center lines, like lanes,
- sidewalks,
- manholes,
- powerlines,
- rails,
- tents, shelters,
- cemetery tombs,
- graveyards,
- sailing boats,
- cars,
- trucks,
- parking lots or spaces,
- bike lanes,
- people,
- trails.
- airplanes,
- trampolines,
- construction sites,
- constructible areas,
- archeological artifacts,
- and many more.
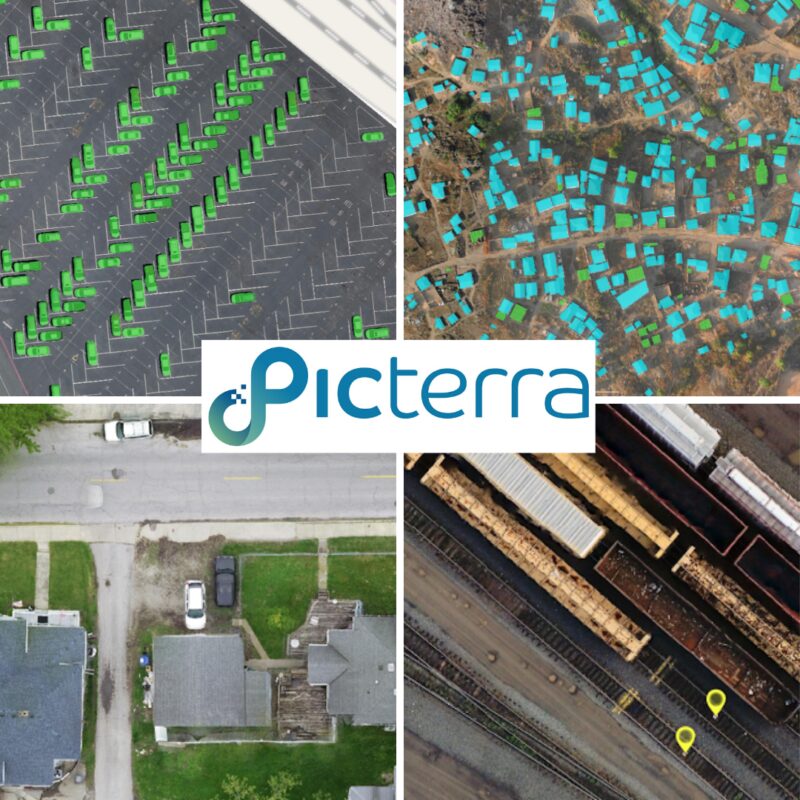

When you want to assess the condition of a road, there are different things you may want to extract, for example, mapping alligator cracks, intersections of cracks (to be more precise), or portholes. You can dig further and categorize different types of damages on the road.

AI is already being used in the design and infrastructure management of cities. It will definitely be an indispensable tool in more and more specific scenarios as we move forward, but here are just a few examples: Mobility is, and remains, a focus. Think about autonomous driving vehicles. Autonomous technology is a broad and complex technology area in and of itself, but the product already includes AI. As the regulatory and compliance features are satisfied for safety, this will become a significant factor in how city transit routes are designed and managed. Spacemaker AI is a company in Oslo that has grown massively over the last year. They claim they “Design better cities with AI”. They use AI technology to maximize the potential of building sites for a given set of criteria, such as views, sunlight, noise, rainwater runoff, access…. literally billions of different factors can be assessed quickly and used to design the architectural footprint of large scale developments. Sewage systems in cities are becoming more efficient with the use of artificial intelligence to predict the quantity of chemicals that should be used to clean up the water runoff after your dirty business, given different potential scenarios such as temporary population increases due to events, planning for normal population growth, precipitation levels etc. With IoT, AI will become the standard way we design most things.
What are other real-life examples of how smart cities are using Artificial Intelligence?
Picterra is highly flexible, and it can be used for very diverse applications. It’s not limited to city-related projects, but it works perfectly in agriculture, forestry, humanitarian help – the sky is the limit, and our Applications Page can give you the big picture. However, in this article, we focus on how smart cities are using Artificial Intelligence, so let’s have a look at a couple of more examples besides assessing road conditions.

Solar panels monitoring
Picterra is also frequently used to monitor solar panels and to estimate the amount of sustainable energy in a particular neighborhood. It’s also possible to analyze roofs and conduct a simulation on whether solar panels can be fitted on them.
Detecting swimming pools
- On Picterra, it’s also easy to detect swimming pools, for example, for the geomarketing purposes or to conduct tax declaration audits. The platform makes it possible to:
- Detect swimming pools or different type of swimming pools,
- Match localization with parcel address,
- Create a visualization portal for marketing or audit teams.
Graveyard management
Rapidly growing cities around the world face the challenge of providing enough cemetery space for their populations. Machine learning is a powerful solution for cemetery management as it helps to estimate when and where there is a need to build more cemeteries. With Picterra, it’s possible to detect graves in just a few clicks.
Detecting green spaces
City managers also use Picterra to map green spaces and assess how sustainable and green are their cities.
And last but not least…
How to get the satellite and aerial imagery?
There are many sources where you can acquire high-quality satellite imagery. We have put together some of them on our Imagery Portal and explained how to easily integrate them with Picterra in the blog post How to get satellite and aerial imagery.
Author:








