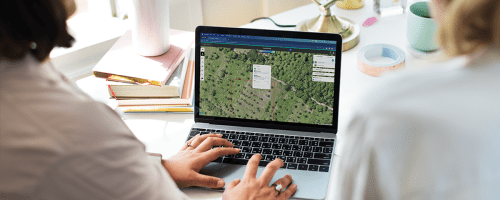
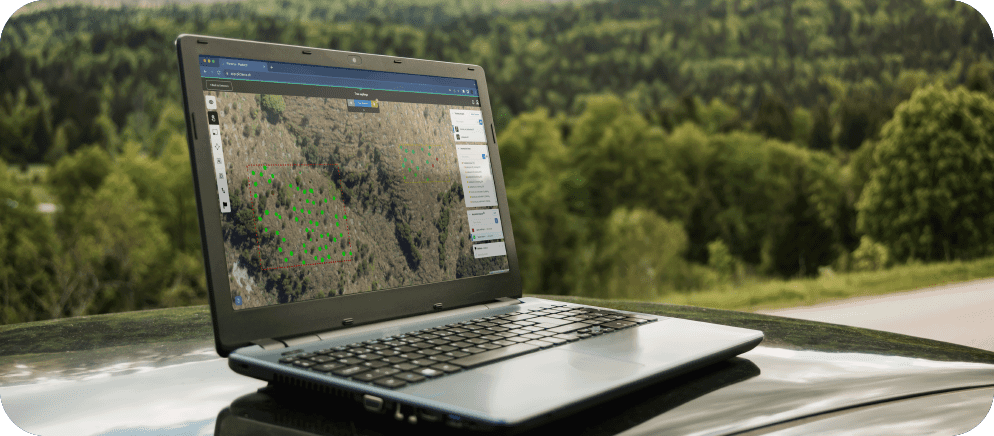
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), approximately 178 million hectares of forest—an area roughly the size of Libya—have been lost worldwide between 1990 and 2020, emphasizing the pressing need for decisive action against deforestation.

The European Parliament recently adopted the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), a groundbreaking law to fight global deforestation, aiming to ensure that products imported into the European Union are not associated with deforestation or forest degradation. This new legislation, also known as regulation (eu) 2023/1115, is a significant step forward, but its implementation and enforcement will require advanced technology to monitor and analyze land-use changes across the globe.
Enter geospatial AI, a cutting-edge technology capable of processing vast amounts of satellite and drone imagery to identify patterns, trends, and risks. This blog post delves into the potential of geospatial AI to bolster the EU’s efforts to fight global deforestation and highlights the crucial role played by companies like Picterra in ensuring EUDR compliance.
Which commodities are affected by the EU's deforestation law?
The EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) is a landmark piece of legislation that aims to halt the import of commodities associated with deforestation into the European Union. The regulation affects a broad range of commodities that have been linked to deforestation and forest degradation around the world. Here are some of the key commodities that fall under the purview of the EUDR:
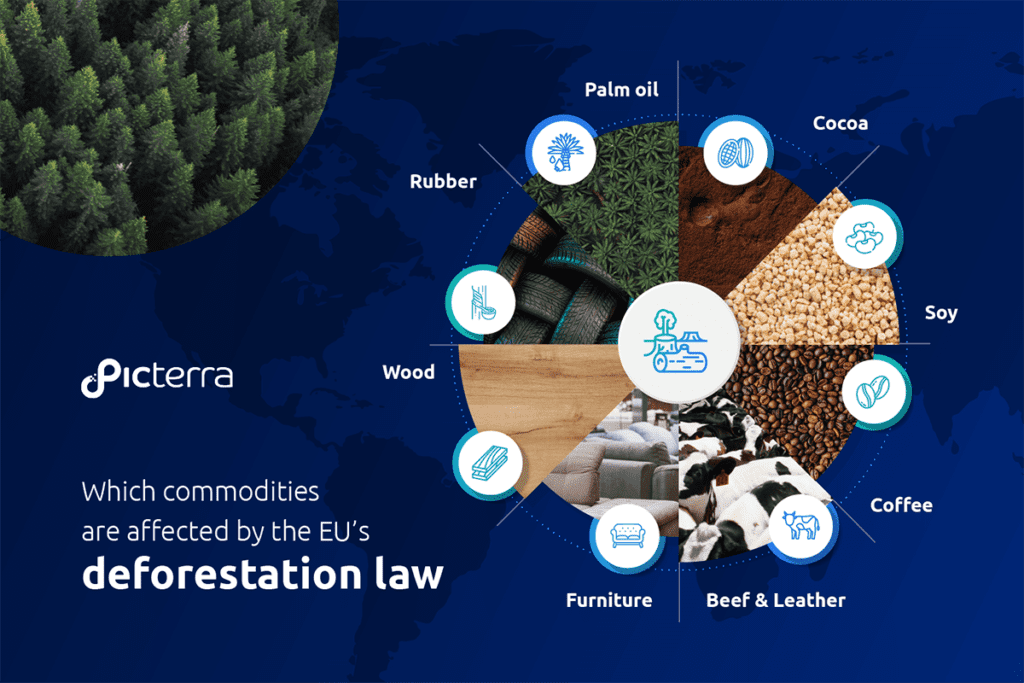
- Cocoa: The production of cocoa, a key ingredient in chocolate, has been linked to significant deforestation, particularly in West Africa. Under the EUDR, chocolate manufacturers will need to ensure their cocoa supplies are deforestation-free.
- Soy: Soy is a major commodity, used in a variety of food products and as animal feed. Soy production, especially in South America, has been associated with extensive deforestation. The EUDR will require soy importers to comply with deforestation due diligence requirements.
- Coffee: Coffee is another commodity that has been linked to deforestation, particularly in regions like Central America and Africa. The EUDR will require coffee producers and importers to demonstrate that their products are not contributing to deforestation.
- Beef and Leather: The beef and leather industries, particularly in Brazil, are significant contributors to deforestation as forests are cleared for pasture. Under the EUDR, companies importing beef and leather products will need to ensure their supply chains are not contributing to deforestation.
- Furniture: The furniture industry, which often relies on timber from around the world, is also affected by the EUDR. Furniture manufacturers and importers will need to demonstrate that the wood used in their products is sourced from deforestation-free areas.
- Wood: The EUDR extends to all wood and wood products, including timber and pulp. These are often sourced from areas of deforestation, and companies will need to ensure their wood supplies meet the EUDR’s deforestation-free certification requirements.
- Rubber: Used in a variety of products, including tires and gloves, rubber plantations have been associated with deforestation in several parts of the world. The EUDR will require rubber importers to demonstrate that their supply chains are not contributing to deforestation.
- Palm Oil: A common ingredient in many food and cosmetic products, palm oil production is a major driver of deforestation, particularly in Southeast Asia. Under the EUDR, companies will need to ensure their palm oil supplies are not associated with deforestation.
Applications of geospatial AI in combating deforestation
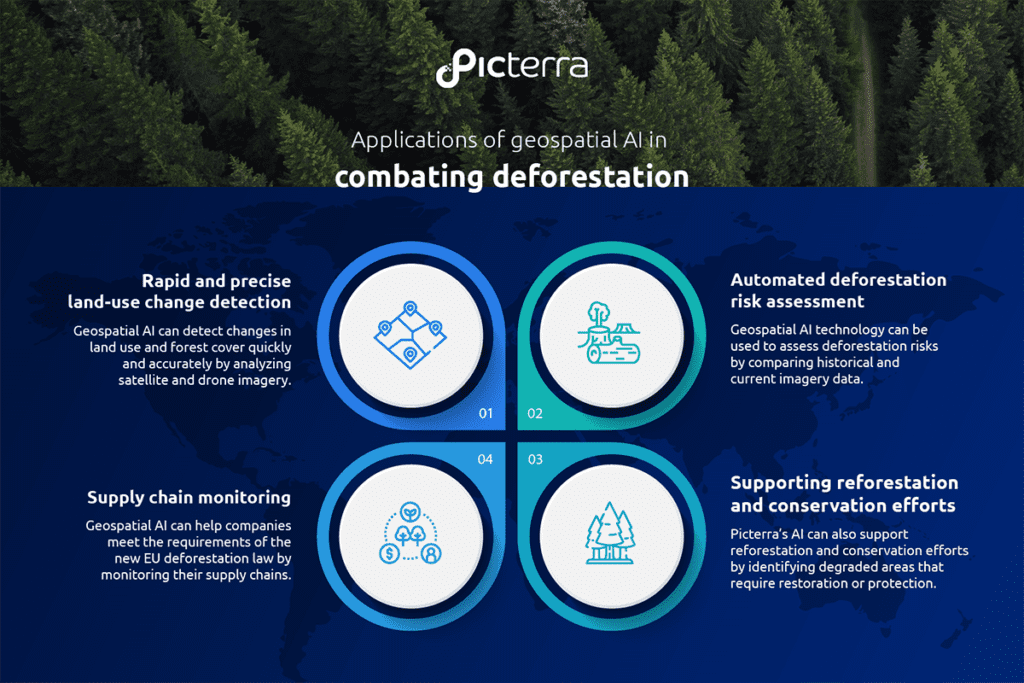
Rapid and precise land-use change detection
Geospatial AI can detect changes in land use and forest cover quickly and accurately by analyzing satellite and drone imagery. This allows for real-time monitoring of potential deforestation or degradation activities in remote locations, ensuring that authorities can quickly identify and address violations of the EU Deforestation Regulation.
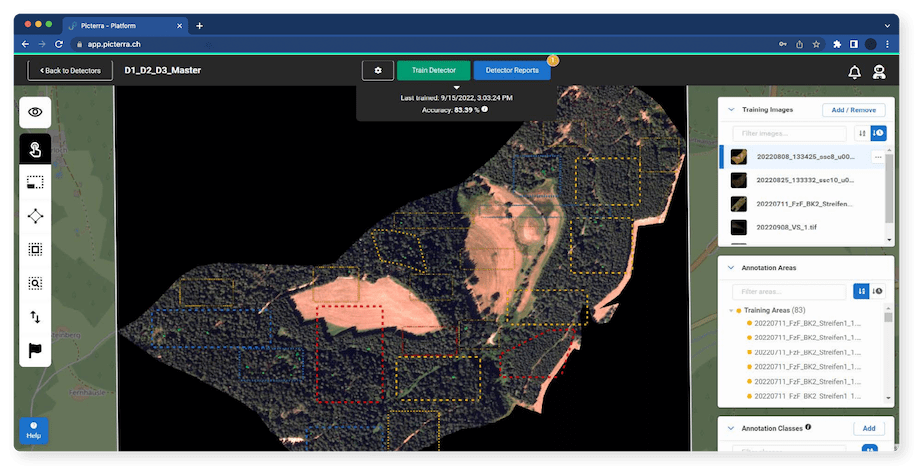
Automated deforestation risk assessment
Geospatial AI technology can be used to assess deforestation risks by comparing historical and current imagery data. By identifying areas with significant deforestation or forest degradation, authorities can prioritize inspections and enforce the EUDR more effectively.
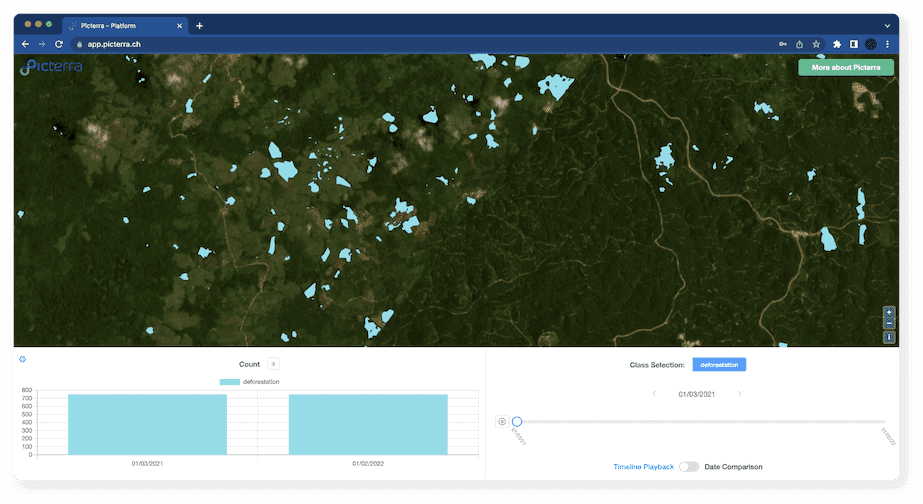
Deforestation-free supply chain monitoring
Geospatial AI can help companies meet the requirements of the new EU deforestation law by monitoring their deforestation-free supply chains. Analyzing satellite and drone imagery enables businesses to ensure that their suppliers are not engaged in deforestation or forest degradation activities and comply with the law’s deforestation due diligence requirements.
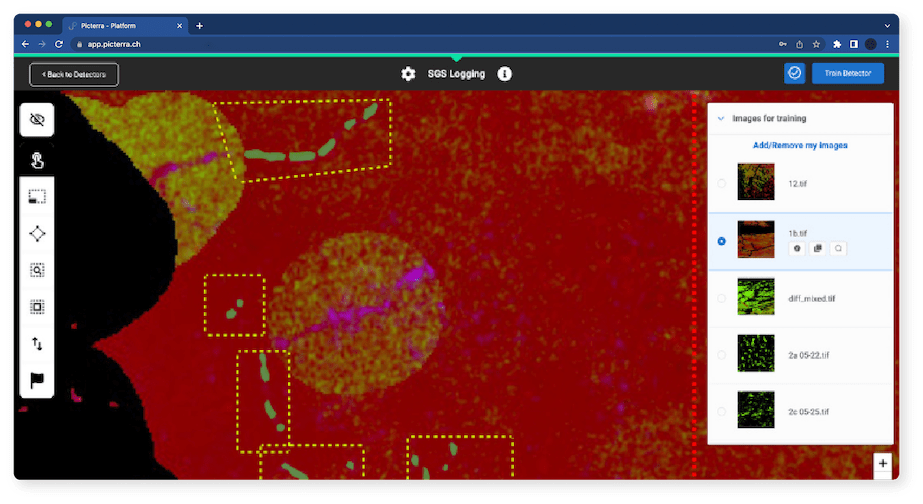
Supporting reforestation and conservation efforts
Beyond enforcement, Picterra’s AI can also support reforestation and conservation efforts by identifying degraded areas that require restoration or protection. This can help governments and organizations allocate resources efficiently and develop targeted, evidence-based strategies for forest conservation.
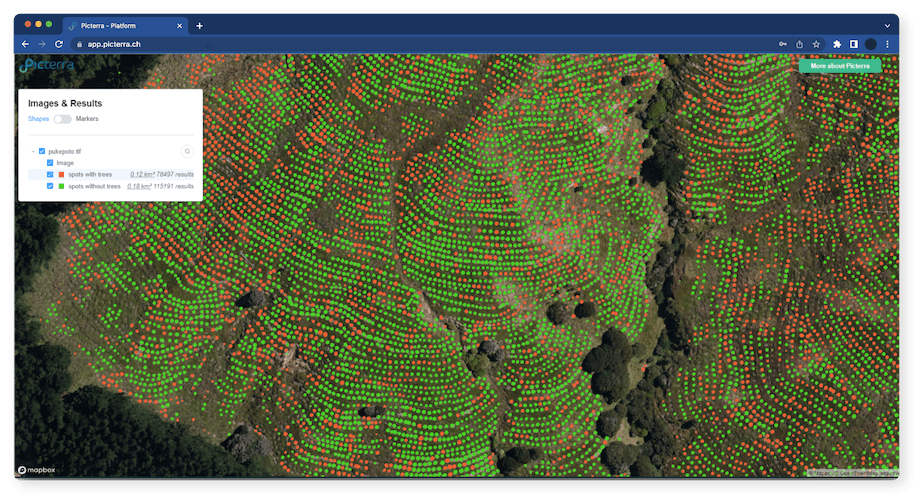
Real-World use cases and success stories
Global Forest Watch (GFW), a platform that provides near-real-time forest change data, leverages geospatial AI to monitor deforestation worldwide. GFW combines satellite imagery and advanced algorithms to identify areas with significant forest cover loss and provide alerts to governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders.
SkyFi, a provider of advanced aerial data and analytics solutions, collaborated with Picterra to track the environmental footprint of mining activities using geospatial AI technology. By combining SkyFi’s high-resolution aerial imagery with Picterra’s machine learning algorithms, they were able to monitor land-use changes, detect early signs of deforestation, and assess the impact of mining operations on surrounding ecosystems. Click here to read more.
The Rainforest Foundation, an organization committed to preserving rainforests and supporting indigenous communities, has partnered with Planet, an earth observation company, to utilize geospatial AI technology. The collaboration aims to monitor illegal logging activities and provide evidence to local authorities to enforce legal actions against violators.
SGS, a leading inspection, verification, testing, and certification company, partnered with Picterra to leverage its geospatial AI technology in monitoring and protecting the world’s forests. By utilizing machine learning and satellite imagery analysis, SGS was able to detect and track deforestation events, assess compliance with forestry regulations, and efficiently report the findings to relevant stakeholders. Click here to read more.
In Indonesia, the government has partnered with organizations such as Global Forest Watch and the World Resources Institute to harness geospatial AI technology in monitoring and enforcing the country’s moratorium on new logging permits. The collaboration has helped the Indonesian government identify and prosecute companies that have breached the moratorium, reducing deforestation rates significantly.
The role of Picterra in the fight against deforestation
As a leading geospatial AI company, Picterra is well-positioned to contribute to the EU’s efforts in fighting global deforestation. By offering state-of-the-art AI and satellite imaging capabilities, Picterra enables governments, NGOs, and businesses to harness the power of geospatial AI for monitoring land-use changes, assessing deforestation risks, and ensuring EUDR compliance.
Furthermore, Picterra’s technology can support reforestation and conservation efforts by identifying degraded areas that require restoration or protection. This can help governments and organizations allocate resources efficiently and develop targeted, evidence-based strategies for forest conservation.
As global deforestation continues to pose a significant threat to biodiversity, climate, and human well-being, the new EU Deforestation Regulation marks a crucial step in addressing this challenge. The power of geospatial AI, as demonstrated through various use cases and success stories, offers the potential to revolutionize the monitoring, enforcement, and mitigation of deforestation worldwide.
With companies like Picterra leading the way in geospatial AI technology, the European Union and its member states can more effectively enforce the new legislation and drive sustainable change. By embracing the potential of geospatial AI, the EU is better equipped to achieve its ambitious goal of halting global deforestation and securing a more sustainable future for all.