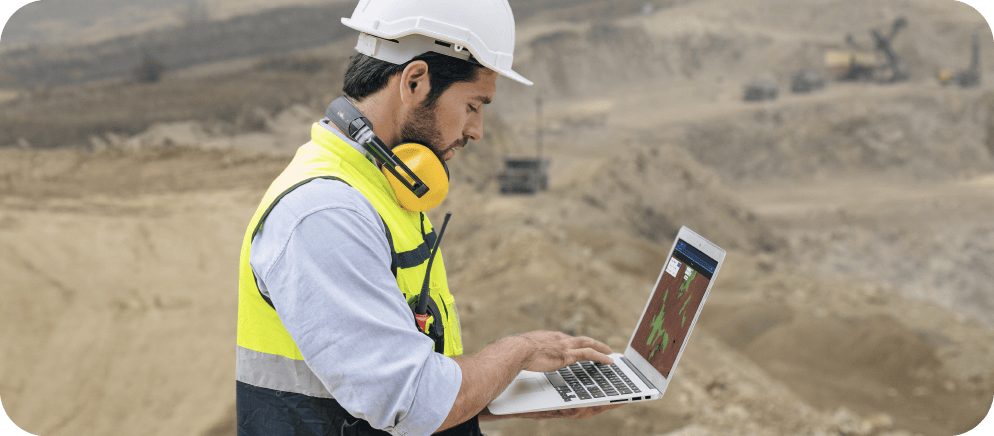
Did you know that incorporating geospatial data in mining operations can lead to a 10-15% reduction in exploration costs? The mining industry increasingly adopts advanced technologies, like geospatial data, to optimize processes and enhance efficiency.
In this blog post, we will explore the world of geospatial data and its benefits for mining operations. We will discuss how geographic information systems (GIS) can provide valuable business insights, showcase some real-world examples, and offer guidance on implementing geospatial data in mining operations.
So, if you’re ready to unlock new possibilities for your mining operations through geospatial data, join us on the journey through the world of GIS technology and its applications in the mining industry.
What is geospatial data?
Geospatial data, a specialized form of spatial data, refers to information about geographic features and phenomena that can be tied to specific locations on Earth. What sets it apart from other data types is its inherent connection to a particular place, enabling users to visualize and analyze patterns, relationships, and trends in a geographic context.
In the realm of mining operations, geospatial data has become an indispensable tool. Using satellite and drone imagery to provide high-resolution, near-real-time insights into the Earth’s surface, allows mining companies to make informed decisions about exploration, planning, and management.
Want to learn more about how geoAI can be used in mining & quarries?
For instance, satellite imagery identifys potential mineral deposits by analyzing the spectral signature of the Earth’s surface, which can reveal the presence of specific minerals. This approach helps mining companies pinpoint areas of interest more efficiently, saving time and resources. Drone imagery, on the other hand, offers a detailed perspective of the mine site, facilitating monitoring of operations, infrastructure, and environmental impacts.
Beyond satellite and drone imagery, other forms of geospatial data can also play a crucial role in the mining industry. For example, geographic information systems (GIS) can integrate and analyze diverse geospatial data sources, such as topographic maps, geological surveys, and remote sensing data. Through GIS technology, mining companies can create detailed operations models, assess potential risks, and optimize mine planning to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impacts.
Benefits of geospatial data for mining operations
Geospatial data offers numerous benefits to the mining industry, from exploration to stakeholder engagement. Let’s discuss the key advantages of incorporating geospatial data into mining operations.
Improved exploration and resource estimation enables mining companies to identify potential mineral deposits more effectively. Analyzing satellite and drone imagery leads to accurate estimations of resources, better decision-making, and increased chances of success in mining operations.
Increased safety and risk management are achieved through geospatial data, as it helps monitor and assess potential hazards like landslides and flooding. Leveraging GIS technology, mining companies can create risk models and implement mitigation strategies for a safer working environment.
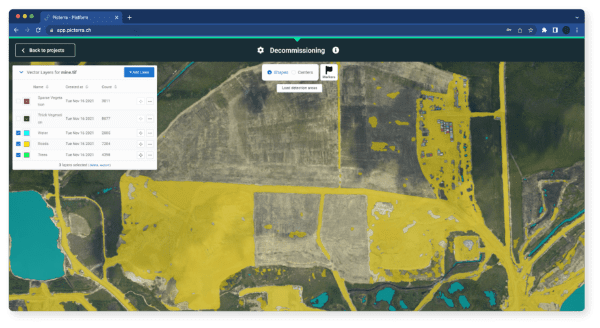
Better operational efficiency and cost savings result from integrating geospatial data into mining operations. By planning and monitoring activities with satellite and drone imagery and other GIS data, delays are reduced, and unnecessary expenses are minimized, leading to higher profitability.
Enhanced environmental management and sustainability are facilitated by geospatial data, helping assess and manage mining operations’ environmental impacts. Satellite and drone imagery can monitor changes in land use, water resources, and vegetation, enabling informed decisions and compliance with regulations.
Improved stakeholder engagement and community relations are another important benefit fostered by geospatial data. Providing a transparent overview of mining operations through satellite and drone imagery facilitates communication and collaboration with stakeholders, building trust, addressing concerns, and promoting sustainable development in mining communities.
What are some real-world examples of geospatial data in mining operations?
The transformative power of geospatial data in mining operations is evident through numerous real-world examples. In this section, we will cover case studies where mining companies have successfully utilized geospatial data, particularly satellite and drone imagery, to achieve their goals.
BHP Billiton, one of the world’s largest mining companies, has embraced geospatial data and GIS technology to optimize its operations. By integrating satellite imagery with other geospatial datasets, BHP has gained valuable insights into geological structures and potential mineral deposits in remote areas. This comprehensive understanding has helped the company streamline its exploration process, reduce costs, and increase the probability of discovering valuable resources.
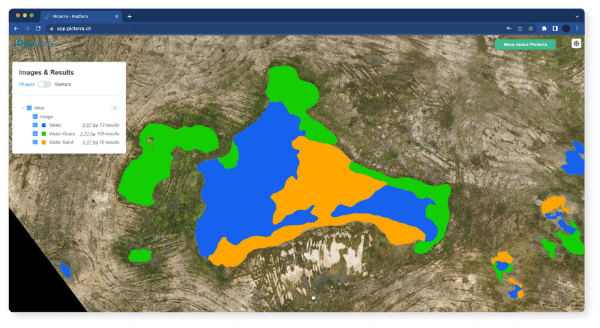
Rio Tinto, another global mining giant, has turned to geospatial data to improve its environmental management and sustainability practices. Utilizing satellite and drone imagery, the company can monitor the environmental impacts of its mining activities, such as land use changes and water resource management. This data-driven approach has enabled Rio Tinto to develop targeted strategies to minimize its environmental footprint and demonstrate its commitment to sustainable mining practices.
Barrick Gold, a leading gold mining company, has successfully employed geospatial data to enhance safety and risk management at its mining sites. By using satellite and drone imagery, the company can identify and monitor potential hazards, such as unstable slopes and tailings dam integrity. This proactive approach to risk management has allowed Barrick Gold to implement mitigation measures, ensuring a safer working environment for its employees and reducing the likelihood of costly accidents.
How to implement geospatial data in mining operations
Successful implementation of geospatial data, especially satellite and drone imagery, requires careful planning and execution across several key areas, including data collection, analysis, technology, staffing, and resources.
For data collection, mining companies must determine the appropriate sources of geospatial data. Satellite imagery providers, such as Planet, Maxar, or Airbus, offer different resolutions, coverage, and pricing options. Other geospatial datasets, like topographic maps and geological surveys, can be obtained from various sources, including government agencies and research institutions.
Data analysis involves using GIS software, such as ArcGIS or QGIS, to integrate and analyze geospatial datasets and visualize patterns. To maximize the value of the analysis, mining companies should define clear objectives and develop a robust methodology. Platforms like Picterra can also be used for machine learning-based analysis of satellite and drone imagery, offering a user-friendly interface to create custom detectors for specific features.
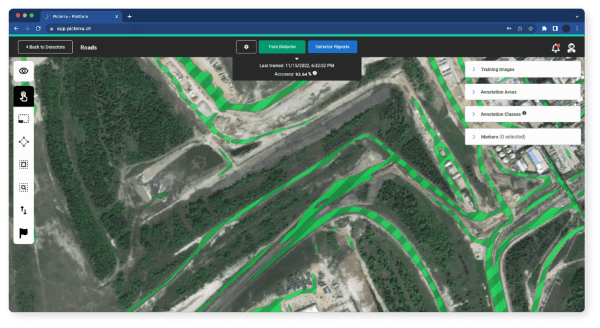
Technology infrastructure is necessary for implementing geospatial data in mining operations. This includes GIS software, high-performance computing systems, data storage solutions, and network connectivity. Cloud-based GIS platforms, like Esri’s ArcGIS Online or Picterra, can provide scalable and cost-effective solutions.
Effective use of geospatial data requires skilled personnel in areas such as remote sensing, GIS, data analysis, and cartography. Companies should invest in professional development and promote a culture of continuous learning to stay current with geospatial technologies.
Resources and tools, like online courses and professional organizations, can support mining companies in getting started with geospatial data and staying informed about industry trends and advancements. Companies interested in machine learning-based analysis of satellite and drone imagery should explore Picterra’s resources for guidance on using the platform effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, geospatial data is an essential tool for the mining industry, providing valuable insights into exploration, operations, and environmental management. By leveraging it, mining companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance safety and risk management, and promote sustainable mining practices.
Although implementing geospatial data requires careful planning and execution, the benefits are worth the investment. With the availability of advanced technologies like satellite and drone imagery, GIS software, and data analytics tools, mining companies can harness the power of geospatial data to unlock new possibilities for their operations.
As the mining industry continues to face challenges such as declining ore grades, increasing environmental concerns, and the need for social responsibility, geospatial data provides a powerful solution to address these issues. By adopting geospatial data, they can become more efficient, sustainable, and profitable, while building trust and collaboration with stakeholders and communities.
Finally, mining companies should embrace geospatial data as a key tool in their operations, investing in the necessary technology and expertise to unlock its full potential. By doing so, they can position themselves for success in the fast-evolving mining industry and create a better future for all stakeholders.